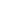How do businesses remain one step ahead of market trends, surpassing competitors? Successful companies do so by constantly reinventing their product offerings to match the changing customer needs. But getting a new product to market is more than just a cool idea — it requires careful planning, testing, and execution.
This guide explores the stages of new product development (NPD) in detail — diving into real-world case studies to ensure maximum success. Regardless if you are iterating on an existing product or creating a completely new one, knowing these stages will aid in minimizing the risks, reducing the time-to-market, and ensuring a good product-market fit. Let’s get started!
What Is New Product Development?
New product development (NPD) refers to the entire process of taking an idea and making it into a product that is ready for sale. This means that it is not just about innovation, developing completely new products or services, but also about small improvements on existing products that allow them to compete or that lead to the introduction of existing products to new markets.
Unlike traditional product development, which iteratively builds on already proven concepts, NPD focuses on the ideation, design, and launch of new solutions that address emerging customer needs. It helps companies remain competitive, respond to market changes, and achieve sustainable growth.
From Idea to Reality: Essential Steps in New Product Development
1. Idea Generation
The first and most critical step of new product development (NPD) is a stage called idea generation, which also serves as the spine to the entire process, as companies throw in potential new ideas to uncover solutions to user pain points or refine existing solutions. During this stage, entrepreneurs analyze market trends, conduct research, and identify gaps in the market that can be filled with innovative solutions.
Key Methods for Idea Generation
SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis also helps to identify the product’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, which can help to improve the product and find opportunities in the market.
For example, if a SaaS company is building out a project management tool, their internal analysis might conduct their SWOT analysis as follows:
🔹Strengths like an intuitive user experience and customizable dashboards.
🔹Weaknesses could be limited integrations to third-party applications.
🔹Opportunities might come in the form of growing post-pandemic demand for remote collaboration tools
🔹Threats can come from long-established competitors providing similar solutions for less. This in-depth investigation allows firms to fine-tune their strategies and improve product development.
Key Internal Stakeholders
Engaging key internal stakeholders offers unique insights into customer needs and operational challenges. For instance, the marketing team might notice gaps in how customers perceive the product and suggest new features that bring in a broader audience, or the Sales Team might notice common objections raised by prospects during the sales process.
The customer support team can highlight persistent pain points in user experience (UX) that might be eroding user satisfaction over time, and the Engineering Team can alert Product Managers to potential technical limitations that might constrain possible solutions or challenge their feasibility. Collaboration with these departments gives you a holistically developed product that will meet all user and business needs.
External Sources: Conducting analytics of outside sources can create valuable intel on competitor strategies, consumer tastes, and industry trends. Learning from a successful fintech player who achieved customer retention through AI-powered financial insights can spark ideas for you to do the same.
Here are some additional research ideas that you can implement:
🔹 Competitor Research: Analyze existing solutions to identify what’s working and where gaps exist.
🔹 User Feedback: Use surveys, interviews, and product analytics to understand user frustrations and preferences.
🔹 Journey Mapping: Visualize the user journey to identify obstacles and areas for improvement.
🔹 Concept Testing: Check initial ideas with rough prototypes to assess feasibility and user interest.
2. Idea Screening
Screening ideas is an essential next step in the new product development (NPD) process making sure to leave the best of the ideas to pursue. This phase analyzes other factors such as market demand, technical feasibility, cost implications, and potential customer benefits to narrow down the options.
The Key Considerations to Look for in an Idea Screening Process:
Customer Value
Does the idea address a big pain point or an urgent need for the target user? For example, a healthcare startup launching a telemedicine platform during the COVID-19 pandemic solved an urgent challenge of remote medical consultations and thus was highly relevant to both patients and doctors. Again, a task management app that enables remote teams to manage their projects in hybrid work settings addresses a timely pain point, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
Technical Feasibility
Is the development of the idea realistic within the existing technology, resources, and timeframe? For instance, a fintech company that wants to offer blockchain payments has to consider whether its existing infrastructure can accommodate the security and transaction speed the business needs. Similarly, an e-commerce platform leveraging an AI-based recommendation engine must ensure that its database and algorithms can scale in a manner that does not impact the overall user experience.
Market Potential
Can this idea even have enough market demand to be worth going after? Market potential analysis enables decision-makers to assess whether an idea can create enough demand to merit development. For example, subscription-based fitness apps took off like never before after the pandemic, given the need to work at home. On the other hand, launching a niche language-learning app intended for a small demographic would have low potential in the market without offering some new differentiator, such as innovative new features or personalized learning paths to set itself apart from existing solutions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Does the anticipated investment pay dividends over the long term? As an example, creating a cloud-based ERP system may require a significant investment at first, but the improved operational efficiency and lowered overhead costs later on would make the expense worthwhile. On the other hand, an e-commerce site implementing a virtual reality-associated shopping experience may sound interesting, but if this involves a target audience that has not yet adopted this kind of technology, it could prove to be a bad investment.
The team discards ideas that do not fit into the long-run framework or have already been proven false. This process helps companies prioritize all the ideas generated and invest their resources in the ideas with the highest potential to be able to launch a successful product.
3. Concept Development
Concept development turns a defined idea into a concrete and structured product proposition. The aim should be to develop a concise guiding plan that explains how the product will address customer pain while ensuring it meets business needs and market demands.
At this stage, you may have several versions of the product concept that will lead you to identify the most viable and attractive solution. For instance, when working on a mobile payment app, there are many ideas to consider: peer-to-peer payments, integration with related e-commerce systems, adding loyalty programs, etc. They test the versions to determine which concept aligns with their customer needs and business goals.
A product concept is an organized template that describes:
🔹Target Market: The type of audience this product hopes to help.
🔹Highlighted Characteristics and Advantages: Lists the core features and benefits that will attract potential users.
🔹Pricing Strategy: Establishes a suggestive price that meets market expectations and perceived value.
🔹Cost Estimate: A high-level estimate of the cost of designing, developing, and launching the product.
Multiple product concepts help businesses broaden their horizons and determine the most attractive and feasible solution. This process ensures that the concepts you land on will not only meet the user’s needs but also align with organizational goals.
Concept validation also aids in analyzing market feasibility. At this stage, potential buyers interact with the product to evaluate its market fit and provide tangible feedback on improvements before moving to development.
Also Read: How Much Does It Cost To Design a Mobile App?
4. Marketing Strategy & Business Analysis (Market Testing)
Typically, once the product idea is validated, the next step is a marketing plan and a detailed business analysis that determines whether the product can be commercially viable. Having a well-defined marketing strategy helps set everything in place for a successful product launch. It focuses on:
🔹Positioning: Defining how the product will be perceived in the market and how it differentiates from the competition.
🔹Pricing Model: Determining a price that balances the value offered to customers with the business placement of the product
🔹Promotional Plan: Outline the channels and tactics to reach the target audience and create awareness.
After the marketing strategy, a business analysis is performed to analyze the product’s commercial viability. This includes:
🔹Sales Forecasts: predict potential revenue and market demand.
🔹Cost Analysis: Determining development, marketing, and operational costs.
🔹Profit Projections: Projecting possible return on investment (ROI) and profitability.
If the results from the business analysis align with the company’s objectives, the product advances to the product development phase. This allocates resources to a concept with both market potential and financial viability.
5. Product Development
This part is focused on substantiating your idea into a full-fledged product that is market-ready. The particular stages in this process will be different based on the development methodology you opt for — Agile, Waterfall, or any other approach that suits your company well.
This stage entails a significant amount of prototype creation and testing, enabling product teams to check their design choices and discover any flaws before handing the designs over to the development team. In prototype testing, real users use the product to give feedback on whether the design meets their expectations. Get in touch with leading Product design companies in India to transform your ideas into innovative, market-ready products with expert design and development solutions.
In this phase, various kinds of prototypes are usually designed and tried:
🔹Low-Fidelity Wireframes: Used for early concept validation of whether the idea resonates with the target audience.
🔹Mid-Fidelity Designs: Developed from the feedback to understand if the layout is better than the previous one and whether it was in alignment with the thoughts of the user.
🔹Prototype Cards High-Fidelity Prototypes: Mimics the final user experience so teams can catch usability errors before full-scale development
Through this iterative process, developers reduce risks, improve user engagement, and contribute to their final product providing a more robust experience.
6. Test Marketing
A crucial aspect of test marketing is the marketing of the prepared product to a sample market to evaluate how the product performs under a devised marketing strategy. The market validation stage is critical in testing product concepts and marketing strategies with real customers before an open launch.
🔹Alpha Testing: It is an internal version of testing where the bugs or performance issues detected in the testing phase get fixed before releasing the software publicly.
🔹Beta Testing: Alternatively, beta testing means launching the product to a pool of real people who then use the product and offer additional inputs on its usability and experience.
Analyzing the results from these tests will help companies optimize their product, improve marketing strategies, and resolve any concerns between their product and customers — guaranteeing a successful and frictionless product launch.
7. Product Launch
At this stage, your product, marketing, sales, and customer support teams should be aligned to ensure a smooth launch and closely monitor the product’s performance. Note that product launch refers to the first time the target market gets access to the product, whereas commercialization is the entire process from product development to market saturation.
Here are some key components to create a winning go-to-market strategy:
🔹Customers: Define your potential customers; who they are, what makes them want to buy something, and develop user personas with detailed information about their objectives and frustrations.
🔹Unique Proposition: Identify how your product is different from competitors and explain why customers should select your product.
🔹Messaging: Create a clear and compelling message that conveys the value of your product to potential customers.
🔹Channels: Choose the optimal marketing channels like email marketing, social media, SEO, and paid ads to get the word out about your product and find your audience.
Lastly, don’t forget to monitor and measure the success of your product launch. If results aren’t as good as you hoped, be ready to adapt and iterate on your plan to get to where you want to be.
Also Read: MVP vs. MLP: How to Choose the Right Product Strategy?
Conclusion
Beyond the simple idea of creating an innovative product, successfully bringing that product to market requires a structured and strategic approach to minimizing risks, maximizing user satisfaction, and ensuring the viability of the business in the long run. By adhering to the seven stages of new product development, you will turn ideas into solutions that address the changing needs of your customers and inform their abilities in their industry.
The information gained at each stage, from idea generation through screening and product launch, can help refine one’s product or service and improve its market fit. Furthermore, iterative development with user feedback helps keep the product relevant to the customer and in line with the market. The key to ensuring the success of the NPD process, to drive the aforementioned sustainable growth and customer loyalty, lies in planning and testing, as well as in the ability to adapt.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture
















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: