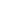Whether you are a college senior aspiring to pursue a career as a traditional developer or an entrepreneur planning to launch your product, you may have come across various terms like No Code/Low Code platforms. While some users suggest that No Code/Low Code is the next big thing, prompting you to reconsider your path.
This situation can be confusing, especially if you are already investing time in learning traditional coding languages like JavaScript. In this blog, we will explore how No Code/Low Code platforms impact the field of development, whether they pose a threat to traditional coding jobs, and what steps you should take to secure a successful career in Development.
Understanding No/Low Code Platforms
No Code/Low Code platforms are designed to simplify the application development process by allowing users to create software with minimal or no coding. As evident from the name, a low-code platform needs minimal coding skills to operate whereas a no-code platform can be used without any development needed. They utilize visual interfaces with drag-and-drop features to build applications, making them accessible to non-programmers. Examples include platforms like Wix, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps.
Benefits of No Code/ Low-Code Development

Low-code development has gained popularity in application development, allowing organizations to build and deliver software and solve problems with unprecedented speed and efficiency. Low-code systems do not require complex coding procedures, make development easier, and allow more people to contribute to the development of the application.
Rapid Development
The advantage of low-level development is that it can speed up the growth cycle. Low-cost systems reduce the time required to develop applications with pre-built components, drag-and-drop interfaces, and automation capabilities. This rapid development process enables organizations to quickly respond to market changes, seize new opportunities, and gain competitive advantage. It consists of traditional siled sections.
Increased Collaboration
These platforms provide environmental visibility and development information, allowing public developers (people with coding limitations) to create applications that meet business needs. This freedom to develop encourages innovation as employees from different departments can contribute their expertise to the application process. Seamless collaboration between IT teams. These platforms can improve communication and coordination of project goals by providing visual feedback.
Reducing Development Costs
This collaboration speeds decision-making, reduces errors, and ensures that applications meet the real needs of the business. Additionally, lean systems increase agility and responsiveness by enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changing needs. saving. By automating workflows and reducing the need for coding, organizations can optimize resource allocation and reduce development costs. Additionally, the ability to develop and deploy applications quickly can increase revenue and ROI.
Optimize Application
Low-code platforms often include good security features, such as testing and evaluation tools, to help ensure the reliability of the application and its operation. By following best practices, low-level systems can help create better applications. Additionally, the ability to quickly revise and tune applications enables continuous improvement and enhances the user experience.
Low-level development has positive effects that can lead to organizational success. By enabling rapid growth, encouraging collaboration, reducing costs, and increasing application efficiency, low numbers allow businesses to innovate, adapt, and compete today.
Developer Implications
The impact of the low-code and no-code platforms has emerged at a time when construction software is undergoing major changes. These platforms are increasing the number of people who can develop applications by simplifying coding requirements. Therefore, the role of the developer is rapidly evolving. This section explains the impact of these platforms on the role of the developer, examining the new skills needed, potential challenges, and opportunities that arise in this changing environment.
Easy and fast Access
Making No-Code (NC) and Low-Code (LC) platforms accessible, this has changed app development for many people. With this tool, users without coding skills can still create functional iOS/ Android apps. This is especially true for business analysts and project managers who need to set up tools quickly. These platforms simplify the development process and enable rapid prototyping. This means ideas can be tested and adapted faster, helping businesses to be agile and responsive to change.
Use Case
The no-code/low-code platform is ideal for certain applications. They are great for creating simple internal tools like task management or job tracking and can also help create simple websites or perform daily tasks. For example, small businesses can use these platforms to create an online store or automate email campaigns. They provide quick and cost-effective IT solutions for simple tasks, making them useful for many users.
Limitations of No Code/Low Code Platforms
These platforms offer a quick way to mobile and web app development, but they also have some disadvantages. Their capabilities may not provide the best solutions or integration services with existing systems. Also, since companies are dependent on a single supplier, relying only on low numbers or no suppliers at all will limit flexibility and hinder performance. These factors should be carefully considered when evaluating the suitability of the platform for the project.
Complexity and Flexibility
No Code/Low Code platforms are user-friendly. But they often fall short when it comes to handling intricate functionalities or detailed customizations. For example, if an application requires specialized features or high performance, No Code/Low Code tools may not be able to meet those needs. In such cases, traditional coding might be necessary to achieve the desired results.
Dependency and Scalability
Another challenge with No Code/Low Code platforms is the risk of becoming too dependent on a single vendor. This can limit your ability to switch to other tools or integrate with other systems. These tools might not handle increased data or user demands as effectively as custom-coded solutions. This can lead to additional costs and complexities when transitioning to a more scalable system.
Foundation and Depth
A solid foundation in traditional coding languages and computer science principles is crucial. Many complex problems and innovative solutions require deep technical knowledge that no-code/low-code platforms cannot provide. Developing traditional coding skills remains essential for building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure and for creating and extending the functionalities of no-code/low-code platforms themselves. These skills provide the depth and flexibility needed to address complex challenges, optimize performance, and innovate beyond the capabilities of low-code platforms.
Career Longevity
Coding skills are highly valued. Traditional developers code, build, and maintain infrastructure. They create and enhance no-code/low-code platforms. But as technology advances, the need for leading IT consulting company grows. New ideas and innovative solutions keep emerging. By investing in traditional coding skills, you ensure career longevity and access to challenging and rewarding opportunities. Coding remains a crucial and invaluable skill in the evolving tech landscape.
What is Traditional Development?
Software development always follows a systematic, step-by-step process, carefully defining each step of the software lifecycle. This rigid model (often exemplified by the waterfall model) dictates the sequential process of defining requirements through design, development, testing, and maintenance. Each stage is completed with detailed documentation and rigorous analysis.
This is successful in an environment such as construction, where the end product is clearly defined and changes are minimal. However, in a dynamic industry such as IT, where change is essential, its limitations are obvious.
Understanding Traditional Development
Traditional software development follows a linear, sequential process. This structured approach involves distinct phases: requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
The Waterfall model is a classic example of this, with each phase completed before the next begins. This method is particularly effective when project requirements are clear and stable, allowing for a methodical and predictable development path.
Traditional Software Development vs. Low-Code/No-Code Development
| Feature | Traditional Software Development | Low-Code/No-Code Development |
| Development Approach | Code-intensive, manual coding | Visual interface, drag-and-drop components, minimal coding |
| Skill Requirement | Experienced developers with deep coding knowledge | Citizen developers with limited coding experience |
| Development Time | Longer development cycles | Faster development cycles, rapid prototyping |
| Customization | High level of customization | Limited customization compared to traditional development |
| Cost | Higher development and maintenance costs | Lower development costs, potential for increased licensing fees |
| Complexity | Suitable for complex, large-scale applications | Best suited for simpler applications and rapid prototyping |
| Control | Full control over the development process | Less granular control compared to traditional development |
| Examples | Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, custom-built applications | Mobile apps, internal tools, business process automation |
Benefits of Traditional Development
In an industry dominated by options of low code and code development, traditional methods often take a backseat. However, its linear approach can still be useful in a project environment. Traditional development comes with unique techniques that make it a good choice for some software development
This method is the foundation of planning and execution, providing a solid foundation for projects where estimation, management, and information quality are important. By understanding the key benefits of traditional development, organizations can make informed decisions about when to use this approach.
Let’s delve deeper into the unique benefits of traditional development.
Highly customizable
Traditional development methodologies often give more freedom and result in better quality and custom products. The sequential approach and clear project scope minimize the need for frequent changes and iterations, allowing teams to focus on delivering the product that the client/users want.
Suitable for Remote Teams
The structured nature of traditional development makes it well-suited for remote teams. Clear project phases and defined deliverables facilitate effective communication and collaboration among geographically dispersed team members. Smaller project scopes often require less frequent interactions, minimizing potential communication challenges.
Strong Security Focus
Traditional development incorporates security measures throughout the project lifecycle. The structured approach allows for the implementation of robust security controls and protocols, protecting sensitive data and systems.
Efficient Project Management
Traditional development often involves smaller, more focused teams, making project management simpler. The clear project phases and defined deliverables provide a solid framework for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments.
Traditional Software Development Use Cases
Traditional software development is great for certain jobs. This works well for things like banking software or government systems where rules are strict and changes are slow. It’s also good for big, complex projects where you need a solid plan to keep things on track. But remember, it’s not for everything. If you’re making an app that changes all the time, or if you don’t know exactly what you want, there are better ways.
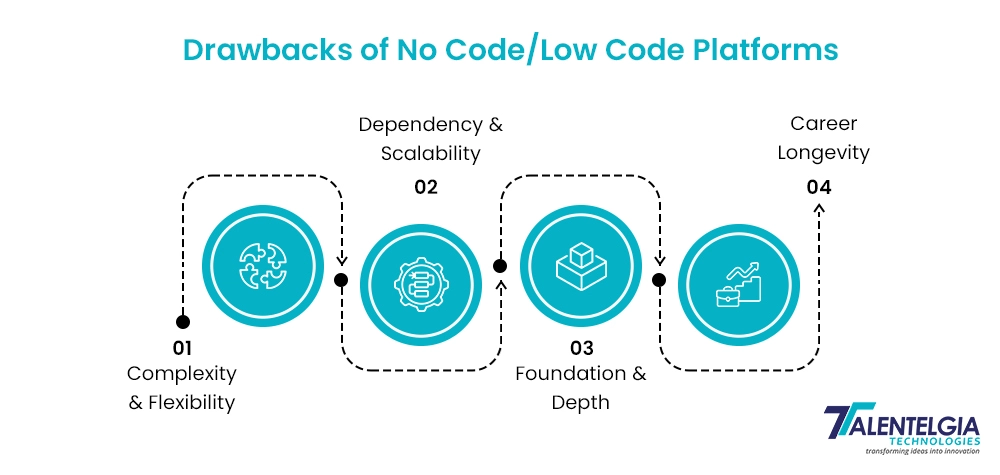
Limitations of Traditional Development
Traditional software development methodologies, while offering structure, present significant hurdles.
High cost involved
Traditional development often takes a longer time and needs more resources. This increases the overall cost of production. However, this also comes with the assurance of custom products that are at par with your requirements.
Delayed Customer Feedback
Traditional approaches often prioritize internal processes over customer input. This delay in incorporating user feedback can lead to products that miss the mark, require costly rework, or, worse, market failure.
Inefficiency and Resource Constraints
The sequential nature of traditional development can introduce inefficiencies. Waiting periods between phases and a lack of overlapping tasks can prolong project timelines and increase costs.
Inefficiency and Resource Constraints
Once a project enters the testing phase, introducing significant changes is often met with resistance due to cost and time implications. This can hinder the ability to incorporate valuable feedback and adapt to changing requirements.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Development

Will No Code/Low Code Replace Traditional Traditional Development Jobs?
The consensus among experienced developers is that No Code/Low Code platforms will not replace traditional development jobs. They make them easier by handling simpler tasks, allowing developers to focus on more complex and valuable work. That is why as technology evolves, the demand for skilled programmers is expected to grow, given the continuous emergence of new ideas and the need for innovative solutions.
Conclusion
Low Code and traditional development each offer unique advantages. Low Code platforms are known for their accessibility, speed, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced collaboration. Meanwhile, traditional coding skills remain indispensable for complex and high-performance projects. Traditional coding skills remain essential. Businesses can leverage both low-code platforms and traditional development to grow and stay competitive. For aspiring developers, ongoing training in coding, project creation, and skill development ensures success and longevity. Embrace integrated systems and leverage low-code and traditional development to thrive in the dynamic tech world.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture
















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: