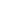Want to create the next Uber, Swiggy, or Airbnb?
These apps work on a very strong idea — the on-demand business model. It provides products or services at the precise time users require them. No delays. No middlemen. Just speed and convenience.
Today’s users want things fast. They demand immediate delivery, real-time updates, and seamless experiences. It creates a need for on-demand apps in every sector. Yet starting an on-demand business isn’t easy. The right model, features, and strategy are needed. One step in the wrong direction could mean the difference between time, effort, and money well spent, and wasted resources.
This blog is your step-by-step guide. We’ll explain what an on-demand business model is. You’ll learn the core features of these apps. We’ll explore the most popular types and help you pick the right one.
Ready to turn your idea into a profitable on-demand business? Let’s dive in.
Top Features Of On-Demand Apps
Below are the essential features that will help you to build an efficient, user-friendly, and competitive on-demand app in the quickly evolving digital landscape. These capabilities not only enhance the customer experience; they also increase retention and propel businesses through sustainable growth. Let’s examine them individually:’
1. GPS Tracking
GPS tracking is one of the important features in most of the on-demand business models. It allows users to check the real-time location of their order or service provider directly through the app. With this feature, users would also be able to track their delivery in real-time, making it more transparent and convenient for them to know about their delivery location and time of arrival.
In food delivery apps, say Zomato or Swiggy, the customer can see the live route of the delivery partner on the map. Likewise, ride-hailing apps such as Uber or Ola use GPS tracking to allow passengers to view the location of their driver and estimate their arrival time.
GPS tracking instills confidence in customers by offering them real-time updates, while also decreasing anxiety and ensuring a seamless user experience. It also aids companies in planning their routes and assigning tasks optimally and addressing delays more swiftly. Simply put, GPS tracking benefits both the user and the service provider.
2. Order Cancellation
In on-demand business models, order cancellation is a critical feature that enables users to make changes to their orders at any time. If a customer finds themselves faced with some unpreventable circumstance, or chooses to change their mind, allowing for cancellation helps build trust and improves the overall experience.
In Instacart, for example, users are able to cancel grocery orders ahead of pickup or delivery. In the event a customer has added the wrong items or has altered their plans, they can cancel the order without a penalty within a specified time frame. Similar gets applied to booking with Airbnb, where guests can cancel the booking based on how the host has set up their cancellation policy. If plans change suddenly, travelers appreciate having the flexibility to adjust without facing steep penalties.
This feature ensures that users feel in control of their transactions, contributing to higher customer satisfaction and fewer complaints.
3. Activity List
The activity list is a must-have feature in on-demand apps that helps users keep track of all their prior orders or bookings. It keeps track of their spending so they can reorder services or products, and can interface with users to help settle disputes.
An example of this is the Lyft app, where users can see their ride history (past trips and charges , and destinations). This allows riders to keep tabs on their spending and easily locate past destinations to re-book. In the same way, in TaskRabbit, the users can access a list of their booked activities, i.e., home repairs and cleaning, in this case.
This feature allows customers to reorder services with a single tap, streamlining the process and saving them time.
4. Push Notification
One of the most powerful features of a mobile app is its ability to push notifications to users in real time. They notify users of important events like order status updates, promotional offers, discounts, and more, helping maintain user engagement in the app.
For example, Domino’s Pizza will send push notifications when you place an order, when the pizza is cooking in the oven, and when it’s out for delivery. This not only keeps customers updated but also adds an element of anticipation. Likewise, Amazon employs push notifications to inform users of flash sales, delivery tracking information, or when their favorite items are restocked so that users can take action on time-sensitive offers.
These notifications not only improve user experience by reducing uncertainty but also drive engagement and help businesses retain customers.
5. Help & Support
On-demand apps need to have help and support features so that when something does go wrong, users feel that they’re being heard and helped. These tools provide fast solutions with options such as FAQs, live chat, email, or direct call assistance.
For instance, Ola has an in-app help center that allows users to report issues like discrepancies in fare or the behavior of the driver. They can log a ticket and see the status of its resolution live. In the same way, Zepto enables users to instantly chat with support in case a product is missing or delayed, providing them with instant solutions without leaving the app.
This is a great feature that builds up the trust of users, increases satisfaction, and demonstrates that the service genuinely cares for its customers, even when everything is not going according to plan.
Types Of On-Demand Business Models
On-demand business models serve as digital hubs, where buyers and sellers connect, engage, and share the space (both physical and online), without any friction, to do business. These platforms make it easy for users to access services with just a few taps while streamlining the process of connecting with providers. Businesses use multi-vendor scripts or a custom solution and have different strategies in placing this model to their advantage.
Now, let us cover the four primary types of on-demand business models with their main characteristics, along with examples from the real world:
1. Business To Business (B2B)
In the B2B on-demand model, one business connects to another through an online platform. It enables companies to quickly and inexpensively access services, such as logistics, staffing, or renting a workspace. Therefore, it focuses on improving operations, eliminating manual work, and increasing efficiency.
For example, Uber for Business provides corporate transportation, Breather App provides flexible office space for teams. TaskRabbit for Business also links companies with qualified contractors for tasks such as cleaning or maintenance.
Ideal For: This model works well for organizations that are trying to scale without committing to the substantial cost of full-time resources.
2. Business To Consumer (B2C)
The B2C on-demand model links businesses directly to individual customers. It provides fast, convenient, and user-friendly services via mobile apps or websites. Customers can order, schedule service, or access content anytime, anywhere.
Airbnb, for instance, enables instant bookings, while companies like Spotify and Netflix deliver on-demand entertainment. In the same vein, Uber and Lyft provide instant rides with several taps.
Ideal for: This approach leans into accessibility, customization, and instant delivery, making it the dominant choice for consumer-facing industries.
3. Print On Demand
Print on Demand is a service that allows you to sell shirts and other products that you designed without having to keep any inventory. Products such as t-shirts, mugs, or phone cases are manufactured only after an order is placed by a customer. This minimizes storage costs and waste, and gives users a choice of the properties they want for the product.
Printing services — for example, companies like Printful and TeeSpring allow creators to upload designs that they put onto products that they then sell through their storefronts. Likewise, sites like Redbubble and Custom Ink connect artists to customers who want something more unique or made to order.
Ideal For: This model combines creativity with flexibility, which is what small businesses, influencers, or individuals need.
4. Subscription Model
The subscription model charges users a recurring fee—monthly, quarterly, or yearly—for uninterrupted access to products or services. It offers ease, flexibility, and predictable costs for consumers.
For example, Amazon Prime provides fast delivery and exclusive deals. Apple Music lets users stream unlimited songs without ads. Meanwhile, Dollar Shave Club delivers grooming kits on a set schedule, and Kindle Unlimited gives readers access to a vast digital library.
Ideal For: This model builds loyalty, ensures consistent revenue for businesses, and keeps users engaged over time.
Here is a brief version of the above information:
| Model | What It Does | Examples | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2B | Connects businesses for services like logistics or staffing | Uber for Business, TaskRabbit, Breather | Companies scaling without full-time hires |
| B2C | Delivers services directly to consumers via apps or websites | Uber, Airbnb, Netflix, Spotify | Fast, user-friendly consumer services |
| Print on Demand | Produces goods only after purchase—no inventory needed | Printful, TeeSpring, Redbubble | Creators, small brands, and side hustlers |
| Subscription | Charges recurring fees for ongoing access | Amazon Prime, Apple Music, Kindle Unlimited | Long-term engagement and predictable revenue |
Top On-Demand Business Models
The on-demand economy is changing how we eat, move, and receive services. By tapping into mobile technology and real-time logistics, businesses across industries are now able to serve customers faster and more efficiently than ever. Let’s explore some of the most profitable and innovative on-demand business models.
1. Food Delivery On-Demand Business Model
The food world is changing from dine-in service to fast, tech-oriented deliveries at an alarming rate. Amid growing consumer demand for convenience, food delivery startups and restaurants are embracing on-demand business models to remain competitive. Customers today want to read menus, order food, and have it delivered to their homes with a few taps of their smartphones.
Industry-leading food delivery services such as Uber Eats, DoorDash, Foodpanda, and Grubhub have raised the bar with seamless ordering and delivery networks. This not only unlocks customer satisfaction but also scalable revenue opportunities for food businesses.
Here’s a brief overview of how the on-demand food delivery process usually goes:
- Customers order through a mobile app or a web app
- Restaurants receive and confirm the order and prepare the food, and assign a delivery partner.
- Delivery agents collect the order and deliver it to the customer’s location in real time.
This seamless flow provides speed, reliability, and transparency, making it a win-win for customers and businesses alike.
Real Life Example: Uber Eats
Uber Eats is a part of the ride-hailing giant Uber, and it completely changed the food delivery industry with its on-demand model. Introduced in 2014 as a natural extension of Uber’s logistics powers, Uber Eats strives to make “eating well effortless for everyone, everywhere.” Its app, for iOS and Android devices, delivers local restaurant menus directly to users’ smartphones, allowing for fast, easy food ordering.
Uber Eats and its business model Uber Eats operate on a multi-sided marketplace model. It connects three important participants:
- Food delivery customers who order through the app
- Restaurant partners who post their menus and prepare the meals
- Delivery partners that collect and take the food to customers’ doorsteps
This dynamic structure combines elements of B2B, B2C, aggregator, and on-demand service models, making it flexible and scalable.
- Revenue Streams: Uber Eats earns revenue from various sources. Well-defined streams allow the company to stay margin positive while serving each segment’s value:
- Commission on Orders: Uber Eats charges restaurants a commission, typically about 30%, on every order placed through the app. This is a huge revenue source, and varies based on the restaurant deal.
- Delivery Fees: Customers pay a delivery fee comprised of a pickup charge, a distance fee, and a base delivery fee. Uber Eats gets a 25% share of the total. (Also, if your order falls below a specified minimum (usually $12), you’ll pay a small order fee, typically $2.
- Promotional Partnerships: Fast-food giants like McDonald’s tend to team up exclusively with Uber Eats for promotional deals. These brands offer higher commissions in return for prominence and marketing visibility in the app.
- Surge or Busy Area Pricing: During busy times, Uber Eats implements dynamic pricing, otherwise known as a “busy fee.” This extra charge is based on demand for, and supply of, nearby delivery partners, similar to the ride-surge pricing model Uber uses.
Who Uses Uber Eats?
Uber Eats has three main customer segments:
- End Customers: These are people using the app to find, order, and track food deliveries. If the user’s face is best for convenience, so the checkout is fast and can pay using different methods.
- Restaurants: By sharing Uber Eats, restaurants have access to a broader customer base without needing to handle their delivery logistics. They also get a digital storefront and marketing exposure.
- Delivery Partners: They’re independent contractors who cycle, drive, or scooter out to pick up and deliver food. They work flexible hours and get paid per delivery, without the hassles of actual employment contracts.
Why the Uber Eats Model Works?
It’s quite simple. Uber Eats delivers specific value to all its users:
- For Customers: The Ordering experience is improved as everything is made instantly available, from a large variety of restaurants, real-time tracking, and estimated delivery time to cashless transactions.
- For Restaurants: Uber Eats also eliminates the need to buy an in-house delivery fleet. It serves the purpose of a marketing channel that pushes orders and brand awareness.
- For Delivery Partners: The model provides flexible income opportunities, allowing partners to create their own schedule in terms of when and how much they want to work — there are no fixed schedules or long-term commitments.
Uber Eats combines technology, logistics, and user experience design to satisfy changing consumer expectations. And by simplifying the process of ordering and delivery, it offers unparalleled convenience and monetizes delighted customers from multiple revenue streams. This case study highlights the importance of a multi-sided platform and how it can drive value in all directions.
2. Courier On-Demand Business Model
The logistics and courier sector is being rapidly transformed, with the advent of on-demand delivery services. These platforms automate critical processes — from receiving delivery requests to tracking and dispatch — enabling smoother and scalable operations.
On-demand delivery services will help manage tasks in an organized manner, track them in real-time, and, more importantly, support running multiple outlets from a single system. Not only this, but it also enhances operational efficiencies, reduces manual work, and decreases overhead costs.
Real World Example: FedEx
FedEx is a global courier offering on-demand logistics services, providing fast and time-sensitive services. It offers air, ground, and freight logistics, catering to one-off parcels through to complex supply chains.
How does It work?
- Customer Access: Individuals or businesses log in via the website or app to book a shipment.
- Service Selection: Customers choose the type of delivery—same-day, next-day, ground, or international.
- Package Handoff: Pickup is scheduled, or users drop off at a FedEx location.
- Transportation & Tracking: FedEx uses its global network (planes, trucks, hubs) to move the package. Customers get real-time tracking.
- Delivery: The item is delivered directly to the customer’s doorstep, often with a signature or proof of delivery.
Revenue Streams : FedEx
FedEx has a very diverse revenue model; as such, the company continues to grow even amid volatile economic cycles. Here’s how FedEx makes money:
- Shipping Charges: Customers pay for ground, air, overnight or international delivery. Costs depend on weight, dimension, distance, and speed. That is the company’s primary source of income.”
- Value-Added Services: In addition, services such as Saturday delivery, insurance, signature-on-delivery, and shipment tracking are available as add-ons, increasing the total value per order.
- Freight and Supply Chain Solutions: FedEx provides e-commerce companies and large corporations with end-to-end logistics management. That involves warehousing, packaging, distribution, and reverse logistics.
- FedEx Office Retail Services: Additional retail revenue comes from in-store services, such as document printing, packaging, passport photos, and business cards.
- Customs and International Trade Services: FedEx offers logistics services, especially seamless for international shipments, as businesses depend on it to coordinate paperwork, duties, and customs clearance.
Who Uses FedEx?
FedEx customers span many market segments:
- Individual Shippers: Individuals sending gifts, documents, or returns via express and ground services.
- Small & medium businesses (SMBs): E-commerce stores & regional vendors requiring dependable delivery partners without having to create their own logistics systems.
- Large Enterprises: Companies in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and tech industries require comprehensive shipping and logistics solutions.
- Government & Public Sector: Time-sensitive, secure, and confidential shipping of documents and equipment.
- Online Marketplaces & E-commerce Retailers: For companies that require support for third-party logistics (or 3PL) from fulfillment to getting the order to the customer’s doorstep.
Why FedEx Works?
FedEx’s model works because it delivers specialized value to each user type:
- For Individual Customers: The platform ensures rapid yet secure deliveries with visible tracking. Depending on how urgent the need is, people can opt for express or economical ground shipping.
- Industry-specific: For Businesses & E-commerce Brands, FedEx serves as an outsourced logistics partner—no need to invest in warehouses, fleets, or shipping staff. Through FedEx Ship Manager and API integration, businesses can manage the entire fulfillment process without any restrictions.
- For Enterprises & Corporations: FedEx provides international shipping, customs clearing, and big freight moving, allowing them to scale globally.
- For Retail Stores: FedEx Office — this is the home of printing, document services, and packaging when it comes to helping you get everything set up for your small business.
3. Transportation On-Demand Model
Ride-sharing is one of the largest and fastest-growing sectors of the on-demand economy. Services like Uber and Lyft have altered daily commuting forever. This removes the hassle of flagging down cabs, waiting for long periods, or dealing with a meter set to a price that you did not agree upon.
Users can book a ride through a mobile app in this model. Nearby drivers get the request, accept it in real time, and go to pick up the user. This convenience allows passengers and drivers to come together easily, no matter their location.
The success of this model is based on real-time GPS tracking, in-app payments, fare estimation, and immediate driver allocation. So, having a smart taxi-booking app is a must for any transportation business that wants to deliver convenience, speed, and reliability to their customers.
Whether you’re starting a local cab service or growing a mobility startup, this model serves as a foundation for addressing the needs of contemporary commuters.
Real Life Example: Uber
Uber is a global mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platform that uses a mobile app to transfer orders between riders and drivers. It undermined taxi companies by providing quicker, cheaper, and tech-enabled transportation services in cities around the globe.
How does the Uber model work?
- Access: Customers log into the Uber app, input their destination, and tap to request a ride.
- Service Selection: Users select their ride based on type (UberX, UberPOOL, Uber Comfort, Uber Black), need, and price.
- Driver Match: Uber’s algorithm assigns a rider to the nearest available driver.
- Trip Execution: The rider is picked up by the driver, the app-determined GPS route is followed, and the trip is executed.
- The payment & rating process: The fare gets charged automatically in the app (by card, wallet, or cash in some regions). Post-trip, users and drivers can rate one another.
Revenue Stream
Uber makes money in several ways related to transportation:
- Commission per Ride: Uber charges a percentage of every fare, usually 20–30%. And in some cases, with fees and surge pricing, that can climb to as much as 50% commission.
- Surge Pricing: Uber employs surge pricing, i.e., dynamic pricing, which increases rates during times of higher demand (e.g., bad weather, rush hours) to maximize revenue per ride.
- Minimum Fare and Booking Fees: Riders must pay a minimum base fare and a booking fee, irrespective of the distance traveled. The presence of these low, fixed charges adds a volume of revenue recurring nature.
- Higher-end options: Uber Black or Uber Comfort have higher fare brackets, resulting in higher commission per trip.
- Subscriptions: Uber One (formerly Ride Pass) is a subscription service that gives users discounted rides and price protection for a monthly fee, providing recurring revenue.
Why It Works?
Uber’s mobility model best succeeds by providing hyper-convenient, scalable, and user-centric experiences:
- For Riders: Available at all times of the day, upfront fare estimates, real-time tracking, cashless rides, and all in one app.
- For Drivers: The platform allows drivers to earn according to a flexible schedule, with few entry barriers, and routing optimization features.
- For Cities: Uber offers a dense, distributed mobility solution that reduces the necessity for personal vehicle ownership and is complementary to public transport.
- For Businesses: Using Uber for Business, companies can better manage employee transport and expense reporting.
- For Growth: The platform is easily scalable across geographies and integrates new features according to local laws and user needs.
That’s why Uber clone app development has become increasingly popular among entrepreneurs aiming to build similar, tech-enabled taxi services with speed and reliability at their core.
Key Factors to Consider While Choosing a Profitable On-Demand Business Model
Wanting to create a successful on-demand service like Uber or DoorDash? It all starts with the right business model. That said, be it a ride-hailing app, delivery app, or home service app, if you want to thrive in the competitive field, you must catalogue the below-mentioned factors that matter for your business and help identify points that can help you stand out.
Follow these key considerations when choosing an on-demand business model:
1. Focus on a Specific Niche
By narrowing down your focus, a good niche allows you to better suit a particular audience. If you become a niche provider rather than a generalist, you can customize your services or offers to meet genuine and unmet market needs. It helps improve customer satisfaction and makes your brand more unforgettable.
Why it matters: Having a niche lets you build an audience with loyal users while limiting competition from larger, more generalist platforms.
2. Identify Your USP
How do you distinguish your business from other companies working in the on-demand space? The USP is essentially the reason a user should choose your app/service over the existing options. It might be quicker delivery, hyper-local availability, better customer care, or even something more specialized.
Tip: Highlight your USP in your branding, app interface, and business marketing strategy to create long-term trust and user engagement.
3. Optimize Your Value Chain
In on-demand businesses, speed and efficiency are important. Evaluate every step in your value chain — from sourcing and fulfillment to delivery and support. Identify bottlenecks, eliminate waste, and automate when you can.
Why this matters: The optimization of the value chain process affects cost savings, user experience, and scalability.
4. Build a Robust, User-Centric Application
Your app or website is the heart of your business. Make sure it offers seamless navigation, fast performance, real-time tracking, secure payments, and clear communication. Whether you’re hiring a tech partner or building in-house, focus on functionality, reliability, and user experience.
Tip: Include relevant keywords like “on-demand app development” or “real-time delivery tracking” to help your content rank.
5. Grow and Strengthen Your Service Network
An on-demand business thrives on the strength of its network—be it drivers, delivery agents, freelancers, or vendors. Invest in recruiting, onboarding, and training your service providers. Also, prioritize customer acquisition and retention through referral programs, loyalty benefits, and active feedback loops.
Scalability insight: A well-managed supply and user network improves customer fulfillment and business longevity.
Conclusion
From ride-hailing apps like Uber to food delivery services like DoorDash and even custom T-shirt platforms like Printful, on-demand business models are transforming how we live, shop, and connect with services.
If you’re an entrepreneur or business looking to tap into this fast-moving space, the key lies in understanding your target audience, ensuring seamless tech infrastructure, and delivering real-time value. Whether you cater to individuals (B2C), other businesses (B2B), or opt for a niche like print-on-demand or subscriptions, this model offers scalable opportunities with lower overheads and higher customer satisfaction.
The future is leaning toward instant gratification, and businesses that can offer speed, flexibility, and personalization will lead the way.
Ready to build your on-demand app or service? Let’s connect and turn your idea into a real-time success story!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: