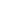Every visual and structural element, from navigation to hierarchy, influences how customers feel as they swipe and click on your mobile app.
This makes creating an interface that guides users effortlessly through an app while completing tasks without unnecessary steps important. When well-executed, a mobile interface design does more than enable functionality. It becomes a tool that nurtures trust and maximizes user involvement.
Read below to find out more about mobile app interface design for mobile.
Types of Mobile App Interfaces
Before deciding on the right approaches, remember that each app requires a tailored design depending on factors like audience and function. Whether a game, social network, or utility, the design must align with users’ needs and goals to help or entertain them effectively.
Different types of mobile app interfaces suit diverse user needs and activities. Below are the four common types:
Principles of Effective Mobile UI Design
When designing any interface, it is important to understand both user needs and the design process. This is where design principles help designers create interfaces that smoothly guide users toward their objectives in an intuitive manner.
Design with a Clear Structure
To start, information architecture sets the foundation by arranging content according to user preferences. It groups similar information and maintains a steady logical flow between screens. Visual design then shapes focus and comprehension, communicating purpose and the next steps throughout the experience.
Consistency of structure and navigation instills predictability, reducing confusion and encouraging working memory. The more organic the navigation feels, the more seamless the overall experience becomes.
Keep Interfaces Simple and Focused
Simplicity comes not from removing features but from prioritizing essentials. Any non-interactive or non-functional elements that introduce noise or distraction should be removed. Too many buttons, choices, or graphics hamper usability by muddying purpose and overwhelming the working memory.
This creates an interface that is easy to learn and simpler to use by showing only the most important components, empowering users, and limiting distractions.
Easy navigation – Make Key Elements Visible
Users should never have to search blindly for important features, wondering how to complete basic tasks. All primary actions, navigation options, and notifications should be on display and simple to access. Avoid concealing components deep in confusing menus or relying solely on cryptic icons lacking explanation.
Clear presentation ensures people can interact easily. So, maintain visual uniformity and customary layouts to help users feel oriented. When all the options are exhibited, the app feels more intuitive and trustworthy.
Provide Immediate and Clear Feedback
Feedback reassures users that the system is responding to their input. Whether it’s a swift animation, a transient message, or a light vibration, feedback instills trust in the app’s responsiveness. It tells users, “Yes, your action was registered.” Without transparent feedback, users might replicate actions, confuse themselves, or assume something is broken.
That is why good UI design service providers incorporate different levels of feedback, from visual cues (like shade changes) to audible responses. These also confirm that every interaction feels acknowledged and intentional.
Design for User Errors
Even regular users of an app make mistakes. That’s why your app should be engineered to withstand these errors. This means offering undo options, clear confirmation dialogs, and input fields that accept common typos or lapses. Rather than penalizing the user, a tolerant UI helps guide them back on course.
Error messages should be constructive, not technical. They should offer actionable advice instead of unclear warnings. When users feel supported, not reproached, they’re more likely to stay engaged.
Apply Consistent Design Patterns
Consistency across an app’s design creates a seamless experience for users. Applying familiar patterns strategically helps users learn an app’s interactions in one area and apply that understanding elsewhere. This lowers the learning curve and makes using the app effortless. It also strengthens a brand’s identity.
Reuse doesn’t mean copying blindly—it means leveraging proven, recognizable designs prudently to add to the usability and efficiency.
Common Mobile Interface Errors
Creating a mobile app’s interface demands more than creativity—it also requires avoiding mistakes that can spoil the user experience. Even the most experienced designers can overlook insignificant issues that tremendously impact how people engage with an app. From misaligned objectives to inconsistent aesthetics, these slip-ups can perplex and ultimately drive users away.
Fortunately, every challenge also comes with a solution. When addressed proactively, these challenges transform into strengths that improve retention, satisfaction, and confidence in an app. Below is an analysis of frequent mobile UI errors and pragmatic solutions to correct them.
Most Common Interface Design Mistakes
| Common Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of Clear Goals | Start with thorough user research. Define clear user journeys and align every element to core tasks. |
| Weak First Impressions | Focus on clean, impactful above-the-fold content. Highlight value immediately with intuitive design. |
| Confusing Onboarding | Create short, interactive tutorials or tooltips. Guide users step-by-step with clear microcopy. |
| Web vs. App Design Conflicts | Design mobile-first. Prioritize touch interactions, simplicity, and vertical navigation patterns. |
| Cluttered & Inconsistent UI | Use whitespace effectively. Stick to a consistent color palette, font family, and component library. |
Lack of Clear Goals
Without a clear understanding of user goals, the interface can become cluttered or misaligned. Always design with specific outcomes in mind.
Weak First Impressions
Users decide within seconds whether they’ll stay on your app. A cluttered or confusing home screen can cause immediate drop-offs.
Confusing Onboarding
First-time user experiences should be simple and educational. Complex or non-intuitive onboarding can discourage users from continuing.
Web vs. App Design Conflicts
Don’t copy-paste your web interface into a mobile app. Mobile design requires a different mindset focused on touch interactions, screen size limitations, and user behavior.
Cluttered and Inconsistent UI
Too many features crammed into one screen can overwhelm users. Consistency in colors, fonts, and button styles builds trust and familiarity.
What is the Interface Design Process?
Creating intuitive mobile interfaces needs strategic planning and setting the right objectives. Each step requires strategic planning to avoid risks that undermine usability. Let’s examine each step of this process.

Step 1: Research & Understand User Needs
Define your target through research: what do they do, hope for now? Interview, analyze competitors, map user behavior, and empathize to uncover real use cases.
Also, work on user personas to ensure that each component assists real needs. Analyze how similar products are used, and note successes and pain points. This principle ensures that your goals align with the user’s needs.
Step 2: Ideation and Concept Validation
After research, work on the user experience. Choose quantity over quality – brainstorm freely through sketches, discussions, and rapid concepts.
From here, narrow down ideas based on feasibility and user goals. Define visual language and construct user journey maps to comprehend the strategy.
You can also choose storyboard user interactions to visualize pivotal scenarios and share these with stakeholders.
Validating concepts ensures that you’re not engineering an interface that solely looks adequate on paper but fails in usage. Ask users if they understand the intention of the app, can envision themselves using it, and how they feel about the navigation flow. This real-time feedback is important for enhanced user interactions.
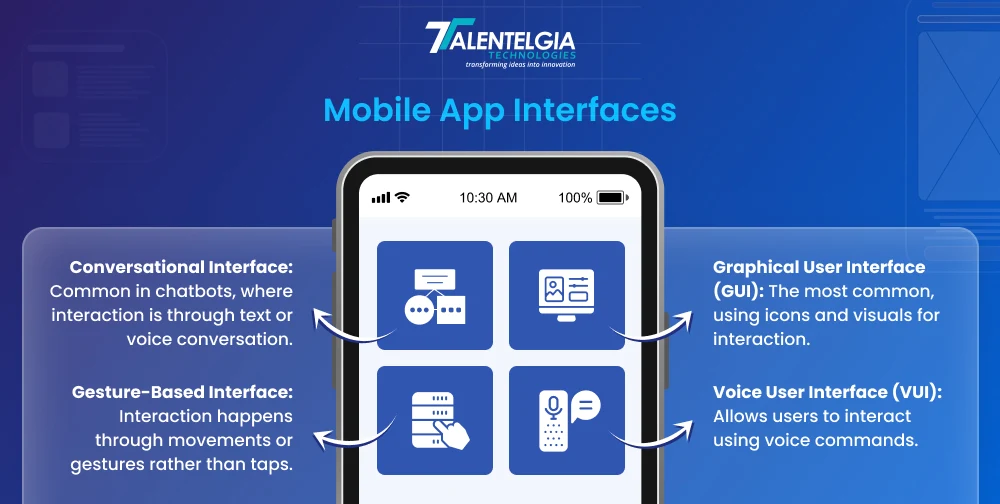
Step 3: Build Wireframes and Prototypes
Once the ideas are aligned and validated, transform them into a tangible form. The first step involves wireframes that map the design of each interactive screen. Do not worry about the aesthetics at this stage, functionality is the key here. These wireframes determine where elements like buttons, images, and text should be placed and how users would progress throughout the application.
After the wireframe is finalized, move on to clickable prototypes that simulate interactive elements, testing the flow and function for further changes.
Tools such as Figma, Adobe XD, and InVision excelled at generating high-fidelity prototypes that emulated the authentic user experience. This permitted both internal teams and stakeholders to evaluate navigation patterns in a realistic setting, pinpoint any logical gaps, and provide early input.
Similarly, a well-built prototype enabled developers to comprehend intended operations in a markedly clearer light, potentially reducing errors of communication later on. It also served as a highly effective means of pitching the concept to investors or testing it amongst prospective users before mobile app development began in earnest.
Step 4: Designing for Accessibility and Usability
Your interface must focus on all the potential users, regardless of their abilities, to make your app easy to use. This goes beyond simple color contrast. Accessibility involves readable text sizes, compatibility with screen readers, gestures for people with motor limitations, and alternate text for images. Following accessibility standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) ensures your app can be used by the largest audience possible.
Usability, meanwhile, focuses on instinctive interactions. Are buttons easily spotted and comprehended? Do users know what to do without an explanation? Are error messages beneficial yet noncritical? A usable app doesn’t make people think too much. Every interaction should feel natural and effortless.
Additionally, consider micro-interactions—those tiny animations or visual cues that exhibit the system working. Whether it’s a spinning icon, a checkbox motion, or a subtle hue shift when pressing a button, these details build feedback loops that boost confidence and reduce friction.
Step 5: Test, Iterate Further
No one is perfect when it comes to mobile app interface design. Once your prototype is ready, share it with users for real testing. Conduct usability tests where users are given specific tasks to complete. Observe how they navigate the app, what confuses them, and where they hesitate. Use screen recording tools, A/B tests, heatmaps, and in-app analytics to capture usage behavior.
Collect both quantitative and qualitative data. Where are users falling off? Which screens do users have high bounce rates from? What do users report to like versus how they act?
Use these learnings to iterate. Occasionally, small adjustments—such as moving the location of a button or streamlining the navigation—can profoundly enhance the user experience. Remember that this is a continuous loop. After launch, keep collecting feedback and deploying incremental updates. Apps that improve based on user data are much more likely to keep users engaged and achieve long-term business objectives.
Best Practices for Inclusive Design
When working on the mobile app interface design, think about the diversity of users you can expect, like different mobile app development languages, impairments, and cultural differences. Provide choices to customize text size, turn on dark mode, or use voice for navigation.
Accessibility in App Interface Design: Use accessible color, labels, and touch targets. Screen reader compatibility is a must.
Voice Interfaces: As virtual assistants gain popularity, voice interfaces become a must. Design voice UI flows that are talkative and sensible.
Gesture-Based Interfaces: Swipe, pinch, tap—gestures need to be intuitive and consistent. Don’t overuse gestures that users might not readily find.
AI-Powered Interfaces: Artificial Intelligence is transforming the way users interact with apps. From personalized suggestions to voice recognition, AI integration makes smarter, adaptive interfaces that learn and change with user preferences.
Top Tools to Create Outstanding App Interfaces
Designing a beautiful and functional interface also requires the use of the right tools. Select a tool that suits your workflow, team, organization, and project requirements.
Below are five of the top tools designers love:
- Figma: Figma is a web-based design tool perfect for collaboration. Offers real-time editing, prototyping, and plugins.
- Sketch: Sketch is my Favorite for UI design with lots of integrations and an active community. Suitable for macOS users.
- Adobe XD: Adobe XD provides robust design and prototyping capabilities. Integrates smoothly with other Adobe Creative Cloud applications.
- InVision: Great for prototyping and user testing. Offers great collaboration and feedback tools.
- Axure RP: This is excellent for professional prototyping with dynamic content and conditional logic.
Conclusion
A well-designed mobile app interface does more than just create a visually pleasing experience. It influences how users use your product, determines their satisfaction, and directly impacts their decision if they will return or not.
When an app is launched, the users expect an easy, intuitive, and pleasant experience. So, the UI should not just be visually pleasing but also effortless to navigate. A good UI can improve retention and engagement and positively influence your brand image.
So, every design element, layout, navigation, and color must be carefully chosen to cater to the users' needs, expectations, and limitations.
Are you a business looking for a team that can give your app an interface that will improve your ROI? Get in touch with us now!


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture














 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: