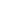Blockchain vs Hashgraph, the two Distributed Ledger Technologies, are transforming data. They are changing how data is shared, verified, and secured in a decentralized manner for the better. While the two technologies operate in the same domain, their mode of operation is completely different.
Blockchain was introduced in 2008 with Bitcoin and had a different approach to data security through its ‘block-by-block’ structure. Hashgraph on the other hand came to light in 2016. IT follows the ‘gossip about gossip approach’ which makes it different from blockchain. This uses a linear structure to group transactions. So how are these technologies making businesses better and what are the key differences and similarities between Blockchain vs Hashgraph?
In this blog, we’ll dive into all these concepts and understand the intricacies of these two DLTs.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that records data in a linear format, where each block contains several transactions. It is completely decentralized which means that it is shared across many computers in a manner that no single person owns or controls it. One of the unique traits of blockchain is that once data is shared and recorded, it cannot be deleted by anyone meaning that it turns into a permanent transaction. This makes it less prone to alteration by potential threats who can otherwise attempt to revise, alter or even remove the data recorded in the blocks.
Moreover, its ability to operate without a single authority enables faster transactions and lower costs. This allows its application in various niches including supply chain management, voting systems, and digital identity verification. Overall, it enhances trust and efficiency while eliminating overhead costs to streamline the entire process.
What is Hashgraph?
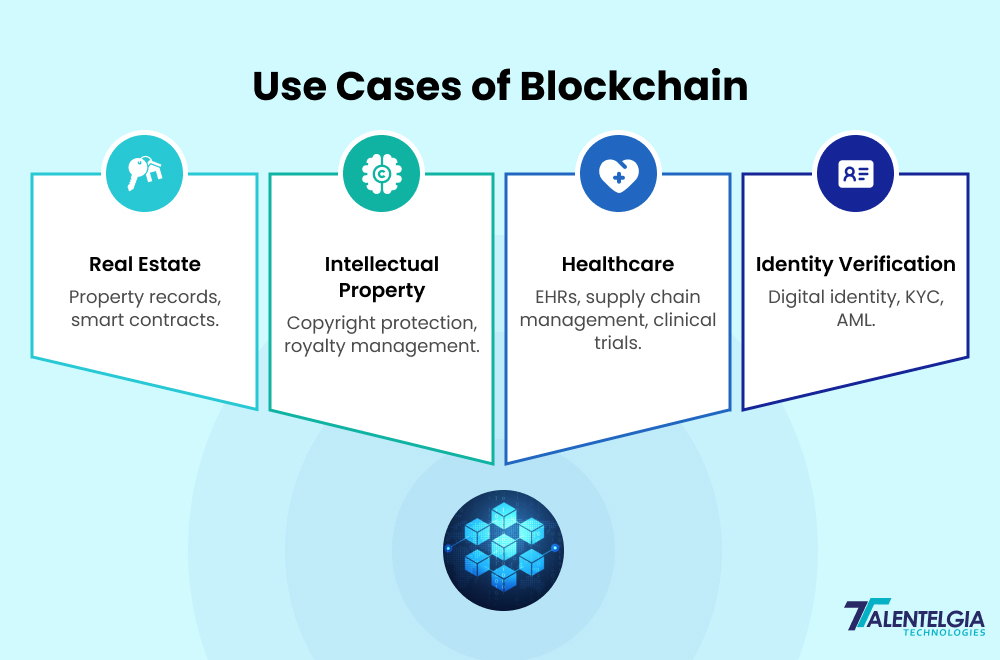
Hashgraph is another Distributed Ledger Technology, introduced in 2016, for securely recording data. While the main goal here is the same as Blockchain, the only difference is the manner of operation. Hashgraph works on the principle of ‘gossip about gossip’ wherein nodes (computers in the network) share data by passing along the information they know. Each ‘gossip’ transaction shares a message inside it, including a timestamp, a virtual signature, and cryptographic hashes.
The computer nodes also share the information source thereby authenticating the transaction.
Another important advantage of Hashgraph is that it eliminates the cons of blockchain, aiming to provide faster data processing speed and reduced costs. This is possible through a system called aBFT (Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance). This allows a network to agree on decisions and continue functioning properly, even with faulty nodes.
What are the Similarities Between Hashgraphs and Blockchain?
While Blockchain and Hashgraph have very different modes of operation, the end goal is the same for both. This can be understood by recognizing that developers created Hashgraph to improve the blockchain framework. Let’s take a look at some of the key similarities between the two DLTs.
Complete Decentralisation
Both Hashgraph and Blockchain operate as completely decentralized technologies, meaning no single entity controls how transactions are conducted or recorded. Instead, computer nodes carry information seamlessly, ensuring everyone can trust the transaction’s authenticity.
Moreover, authenticating each transaction significantly reduces the risk of fraudulent activity. Each node maintains a copy of the original transaction to ensure that even if one node goes down, the entire data remains uncompromised. As a result, both technologies offer a reliable and secure method of data processing. This builds long-term user trust and transparency.
Immutability
Immutability means that once the system writes a particular transaction, it never changes or alters it. This significantly reduces the risk of potential threats attacking the data. Moreover, since the data is permanent, the system will trace any attempt to alter or erase it.
This ensures long-term system transparency and it builds a sense of confidence and reliability amongst the users. This is particularly useful in sectors like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. In these industries, transaction reliability is essential, and data compromise is unacceptable.
Scalability
Scalability in the context of Hashgraph and Blockchain refers to their ability to process and store large data sets without compromising security. Hashgraph utilizes its unique “gossip about gossip” approach, which allows for fast data sharing among nodes. In contrast, Blockchain relies on layer-2 solutions to enhance transaction throughput.
This ability to provide scalability plays a vital role in supporting real-world mobile applications across various industries. This includes finance and healthcare, where large volumes of data and rapid processing times are essential for success.
Key Differences: Blockchain vs Hashgraph
| Feature | Blockchain | Hashgraph |
| Data Structure | A linear chain of blocks | Directed acyclic graph (DAG) |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Virtual Voting |
| Security | Strong cryptographic algorithms | Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Speed | Relatively slow | Fast |
| Energy Consumption | High (especially for PoW) | Low |
Both Hasgraph and Blochain have a wide range of differences that make them competitors in the DLT domain. Securing transactions and providing cost and process efficiency are their main goals but their underlying structures are very different. Let’s understand the key differences when it comes to both these DLTs.
Security
Hashgraph and Blockchain deploy two very different mentors for securing your transactions. Blockchain makes use of mathematical algorithms to secure the data in a linear format. In case a potential threat attempts to alter or remove the data, the system alerts the entire network enabling them to take necessary action against potential tampering.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, deploys a feature called aBFT, which stands for Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance, to ensure that your data is safe from potential threats. By tracing every transaction that occurs in the network, Hashgraph can improve previous transaction versions and take prompt action to enhance reliability and efficiency.
Making the right decision about which DFT will suit your specific business needs depends on the kind of security you require. For instance, a bank may opt for Blockchain technology because of its robust security measures and transparency when handling sensitive customer data. On the other hand, a supply chain company might choose Hashgraph due to its speed and efficiency in tracking multiple transactions simultaneously.
Consensus
Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain use different methods to agree on transactions. Hashgraph uses a technique called virtual voting, which lets participants reach a consensus without sending individual votes across the network. Instead, each member looks at their copy of the Hashgraph to calculate the votes. This saves bandwidth and ensures everyone follows the same rules.
On the other hand, Blockchain does not go for any particular approach for reaching consensus; It depends entirely on the platform or cryptocurrency. Common methods include Proof-of-Work, where participants prove that they’ve done their part to validate transactions, and Proof-of-Stake, where validators prove they are providing value in the network. The best consensus method depends on the specific cryptocurrency and the needs of the user.
For instance, if a cryptocurrency focuses on being energy-efficient, it might choose Proof-of-Stake, but if it prioritizes security, it might opt for Proof-of-Work. Understanding these differences can help businesses select the right technology for their needs.
Which one is the right fit for your business?
With the above-mentioned similarities and differences, a better understanding of what the two DLTs are has been provided. The question remains, which one is the best for your business in this BlockChain vs Hashgraph debate?
Let’s understand this with the help of a few quick references.
You can opt for Hashgraph if you need a DLT that offers:
Fast Data Processing
Hashgraph processes data at high speeds, easily handling between 250 to 50,000 transactions per second. This demonstrates its exceptional efficiency. This makes it better for your business if you need real-time data processing such as financial systems or supply chain management.
Moreover, fast data processing will also reduce user wait time thereby building long-term customer loyalty.
Minimum Environmental Footprint
With rising concerns around climate change and the need to reduce carbon footprint, businesses are turning to technologies and processes that are cost-efficient and environment-friendly. Hashgraph will help you achieve this goal by offering reduced environmental impact than Blockhain which can be extremely resource intensive.
For instance, between 2020-21, blockchain consumed 173.42 TWh of electricity just for mining purposes. Hashgraph on the other hand makes it a more eco-friendly option through its consensus algorithm.
On the other hand, you can go for Blockchain if you need a DLT that offers:
Open Source Community
If customization is at the top of your priority list, blockchain is the DLT for you. It has a large, growing open-source community. This means that there are many opportunities for blockchain developers to customize the blockchain solutions accordingly. For instance, platforms like OpenChain and Corda are open-source blockchain projects that enable businesses to enhance their business operations based on specific operational requirements.
Mining For Data Verification
Blockchain will be the right fit for you if your project relies on cryptocurrency mining as the main pillar to succeed. Blockchain networks rely on mining as a method of transaction verification to secure and maintain data integrity. Hashgraph eliminates the need for mining in the transaction verification process, allowing you to focus on what your project requires and intends to accomplish.
Blockchain Vs Hashgraph- What will be the Future?
As we move forward, it is important to note that Blockchain and Hashgraph have unique advantages of their own that might shape their adoption in different industries. The debate on BlockChain Vs Hashgraph has to settle on having a balance between both the DLTs. Blockchain, as the more mature technology, will probably continue to enjoy dominance in areas that depend more on cryptocurrency development, decentralized finance, and other areas. Its robust community of developers, alongside its flexibility, will certainly be a worthwhile asset to financial systems, gaming, and more such sectors.
Hashgraph, on the other hand, has better transaction speed alongside a much more secure architecture. Moreover, given the increase in focus on sustainability and the need for real-time data processing. Hashgraph can emerge to be a leader in supply chain management, telecommunications, and real-time financial services.
The Future will probably see both technologies coexisting together with each finding its specific niche.


 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services
 Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services
 E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce Development Company
 Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Fintech Web Development
Fintech Web Development Blockchain Fintech Development Company
Blockchain Fintech Development Company
 E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services
 Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company
 Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company
 Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company
 Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design
 AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System
 AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  SaaS App Development
SaaS App Development Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database Development
Database Development Ruby on Rails Development
Ruby on Rails Development Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development  Web Development Services
Web Development Services  Laravel Development
Laravel Development  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  .Net Development
.Net Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics Car Wash App
Car Wash App Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services LMS Development
LMS Development CRM Development
CRM Development DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development API Development
API Development Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 Healthcare App Development Services
Healthcare App Development Services Real Estate Web Development Services
Real Estate Web Development Services E-Commerce App Development Services
E-Commerce App Development Services E-Commerce Web Development Services
E-Commerce Web Development Services Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company
Blockchain E-commerce
Development Company Fintech App Development Services
Fintech App Development Services Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development Blockchain Fintech
Development Company
Blockchain Fintech
Development Company E-Learning App Development Services
E-Learning App Development Services Restaurant App Development Company
Restaurant App Development Company Mobile Game Development Company
Mobile Game Development Company Travel App Development Company
Travel App Development Company Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design AI Traffic Management System
AI Traffic Management System AI Inventory Management Software
AI Inventory Management Software AI Software Development
AI Software Development AI Development Company
AI Development Company ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development Smart contract development company
Smart contract development company NFT marketplace development services
NFT marketplace development services IOS App Development
IOS App Development Android App Development
Android App Development Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App
Development Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development Web App Development
Web App Development Flutter
Flutter React
Native
React
Native Swift
(IOS)
Swift
(IOS) Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android) MEAN Stack Development
MEAN Stack Development AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development Web Development Services
Web Development Services Laravel Development
Laravel Development LAMP
Development
LAMP
Development Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services Automated Testing
Automated Testing Manual
Testing
Manual
Testing About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia Our Team
Our Team Our Culture
Our Culture















 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: