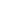Companies committed to growth know that technology can help employees focus on more important tasks. Among these technologies, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) stand out. They can significantly reduce costs, increase efficiency, improve customer and employee experience, and provide rapid turnaround. Use them together for complete automation.
The current global RPA market size has been predicted to reach 30,850.0 Million By 2030.
On the other hand, the AI market is said to be at $1,811.75 Billion By 2030.
Although there is much debate about these technologies, many people remain confused about the differences between the concepts, how each of them should be implemented, and how all of them complement each other.
Businesses today have both simple tasks and complex decision-making processes; hence they need both types of technology. RPA is great for simple, step-by-step processes. On the other hand, AI is better at improving human decision-making in complex processes.
RPA and AI can significantly boost operational efficiency and transform your company’s operations.
Now let’s understand how AI and RPA are different with the help of an example. Website Chatbots are very commonly used nowadays and let’s learn how website chatbots will behave differently when it comes to the chatbot is implemented as RPA or AI.
Below we have mentioned the practical uses and behavior of the chatbot depending on if it is RPA or AI.
RPA Chatbot Capabilities
Automate repetitive tasks: RPA chatbots are great for tasks that are repetitive and follow set rules, like data entry, filling out forms, and processing transactions.
Workflow automation: They can automate the entire business process by interacting with various applications & systems and tracking human behavior.
System Integration: RPA chatbots can integrate with many legacy systems and applications to extract and access data without the need for APIs.
AI Chatbot Capabilities
Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI chatbots use NLP to understand and answer user questions, allowing them to manage complex conversations.
Learning and Adaptation: They can learn from interactions over time, improving their responses and understanding user goals.
Personalization: AI chatbots can give customized responses and recommendations based on your data and past interactions.
What is RPA?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is defined as an advanced technology solution that consists of bots to do repetitive or customized work that may be done manually. These tasks can include data entry, processing transactions, managing data, and responding to simple customer service queries. RPA tools are programmed seamlessly to mimic operations that human beings perform using their keyboards, mouse, and other interfaces.
RPA is ideal for business processes like:
- Opening emails and attachments
- Cleaning and formatting Excel sheets
- Retrieving and entering data in different applications
- Extracting data from structured documents
- Performing predefined tasks
- Handling periodic reporting, data entry, and analysis
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI adds man-like decision-making processes to take up complex tasks neither thought to be achievable by RPA. It uses AI algorithms to quickly process big data, allowing AI to learn from data patterns and thus simplify complex processes.
It’s very essential to learn the basic concepts on artificial intelligence in order to understand the full potential that it can achieve and how it’s applied to a variety of tasks.
Machine learning is the major component of artificial intelligence, which allows machines to identify the moment and give better results. It uses algorithms and design methods to find patterns in data, make predictions or decisions, and improve performance through operations.
Different Branches of Artificial Intelligence
NLP seeks to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It enables machines to process and analyze huge amounts of natural language data, performing tasks such as translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and writing text.
Computer Vision
This area of artificial intelligence allows computers to interpret and understand information contained in images or videos. Computer vision algorithms are used for tasks such as object recognition, image classification, face recognition, and image rendering.
AI/ML enhances automation and human experiences by:
- Handling data from semi-structured and unstructured documents
- Understanding conversations through natural language processing
- Identifying processes and tasks for greater automation
- Making accurate predictions based on large data sets
AI adds human-like intelligence to RPA automation. For instance, AI can intelligently extract data from various documents, while RPA quickly enters that data into any desktop or web-based system.
RPA vs AI – Understanding Key Differences
Augmented Intelligence for Complex Decision-Making
RPA performs routine tasks,While, AI makes complex, accurate, and adaptive decisions when dealing with unusual or unstructured data. Whereas, integrating AI with RPA can improve business decision-making.
Scalability and Adaptability
Both AI and RPA can manage large and complex processes, but AI is more flexible. AI learns and adapts based on data and feedback, making it highly versatile. In contrast, RPA often requires manual adjustments or programming for new tasks, making it less adaptable.
Continuous Learning and Process Optimization
Integrating AI into RPA operations allows the system to learn from tasks performed by RPA, identify patterns, and recommend improvements. This creates a cycle of continuous improvement where AI insights improve RPA processes, reducing costs, increasing productivity, and increasing return on investment over time.
Adaptive Compliance and Risk Management
AI’s ability to analyze big data and identify anomalies or risks enhances RPA-driven processes with flexibility and risk management. Instant risk assessment and compliance monitoring to keep up with changing regulations and reduce losses from non-compliance.
RPA vs AI – Making the Right Choice
A good approach is to start by implementing RPA first and then expand automation using AI.
Begin by finding quick wins by analyzing the complete workflow of a process and identifying rule-based tasks that can be automated with RPA.
Processes suitable for RPA typically exhibit the following characteristics:
Characteristics of RPA
- Involve large amounts of structured data
- Are repetitive and time-consuming
- Follow clear rules and instructions
- Require minimal human intervention
- Involve data handling across different systems
Implementing RPA creates a solid foundation for your digital systems. Once RPA is in place, it’s easier to introduce AI for more complex tasks.
AI-driven automation works best in the following areas:
- Processes that require predictive analytics (e.g., inventory forecasts, loan defaults)
- Processes that are highly variable and don’t follow set rules
- Processes that use unstructured or semi-structured data
For example, consider invoice automation. If invoice formats vary widely, Machine Learning (ML) models can train bots to read, interpret, and learn from different data sets, making invoice processing more accurate and efficient.
Also Read: AI Development Companies in India
Conclusion
AI represents the forefront of advanced technology that revolutionizes several industries. If you are looking for smart solutions, AI offers remarkable capabilities, Whereas if your priority is cost-effective solutions that make your repetitive tasks easier, Robotic process automation (RPA) is a great choice.
When deciding between RPA vs AI, a pragmatic approach is to start with RPA for quick wins in automating rule-based tasks. Once a solid foundation is established, AI can be integrated into a variety of tasks involving predictive modeling and unstructured data. These technologies streamline daily operations, allowing employees to focus on more productive, value-added activities.


 About Talentelgia
About Talentelgia  Our Team
Our Team  Our Culture
Our Culture 
 AI Software Development
AI Software Development  AI Development Company
AI Development Company  AI App Development Services
AI App Development Services  ChatGPT integration services
ChatGPT integration services  AI Integration Services
AI Integration Services  Generative AI Development Services
Generative AI Development Services  Natural Language Processing Company
Natural Language Processing Company Machine Learning Development
Machine Learning Development  Machine learning consulting services
Machine learning consulting services  Blockchain Development
Blockchain Development  Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain Software Development  Smart Contract Development Company
Smart Contract Development Company  NFT Marketplace Development Services
NFT Marketplace Development Services  Asset Tokenization Company
Asset Tokenization Company DeFi Wallet Development Company
DeFi Wallet Development Company Mobile App Development
Mobile App Development  IOS App Development
IOS App Development  Android App Development
Android App Development  Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-Platform App Development  Augmented Reality (AR) App Development
Augmented Reality (AR) App Development  Virtual Reality (VR) App Development
Virtual Reality (VR) App Development  Web App Development
Web App Development  Flutter
Flutter  React Native
React Native  Swift (IOS)
Swift (IOS)  Kotlin (Android)
Kotlin (Android)  Mean Stack Development
Mean Stack Development  AngularJS Development
AngularJS Development  MongoDB Development
MongoDB Development  Nodejs Development
Nodejs Development  Database development services
Database development services Ruby on Rails Development services
Ruby on Rails Development services Expressjs Development
Expressjs Development  Full stack development company
Full stack development company  LAMP Development
LAMP Development  Custom PHP Development
Custom PHP Development  User Experience Design Services
User Experience Design Services  User Interface Design Services
User Interface Design Services  Automated Testing
Automated Testing  Manual Testing
Manual Testing  Digital Marketing Services
Digital Marketing Services 
 Healthcare
Healthcare  Finance And Fintech
Finance And Fintech  E-Commerce And Retail
E-Commerce And Retail  Education
Education  Food And Restaurant
Food And Restaurant  Real Estate
Real Estate  Travel
Travel Ecommerece Web Development
Ecommerece Web Development  Real Estate Web Development
Real Estate Web Development  Automotive Web Design
Automotive Web Design Finance Web Development
Finance Web Development  AI Traffic Management System Development
AI Traffic Management System Development  AI Inventory Management Software Development
AI Inventory Management Software Development  Blockchain Ecommerece Development Company
Blockchain Ecommerece Development Company  Fintech Blockchain Software Development
Fintech Blockchain Software Development  Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services
Ride-Sharing And Taxi Services  Food Delivery Services
Food Delivery Services  Grocery Delivery Services
Grocery Delivery Services  Transportation And Logistics
Transportation And Logistics  Car Wash App
Car Wash App  Home Services App
Home Services App ERP Development Services
ERP Development Services  CMS Development Services
CMS Development Services  LMS Development
LMS Development  CRM Development
CRM Development  DevOps Development Services
DevOps Development Services AI Business Solutions
AI Business Solutions  AI Cloud Solutions
AI Cloud Solutions  Blockchain Product Development
Blockchain Product Development  Cryptocurrency Wallet Development
Cryptocurrency Wallet Development 






 Business: +91-814-611-1801
Business: +91-814-611-1801






 Write us on:
Write us on:  Business queries:
Business queries:  HR:
HR: